MVC实现原理
流程: 一个request由DispatcherServlet接收到,根据请求的url去handlerMapping取到对应的controller,调用controller的方法,返回ModelAndView,通过ViewResolver解析,得到View,最后渲染。
首先贴上时序图:
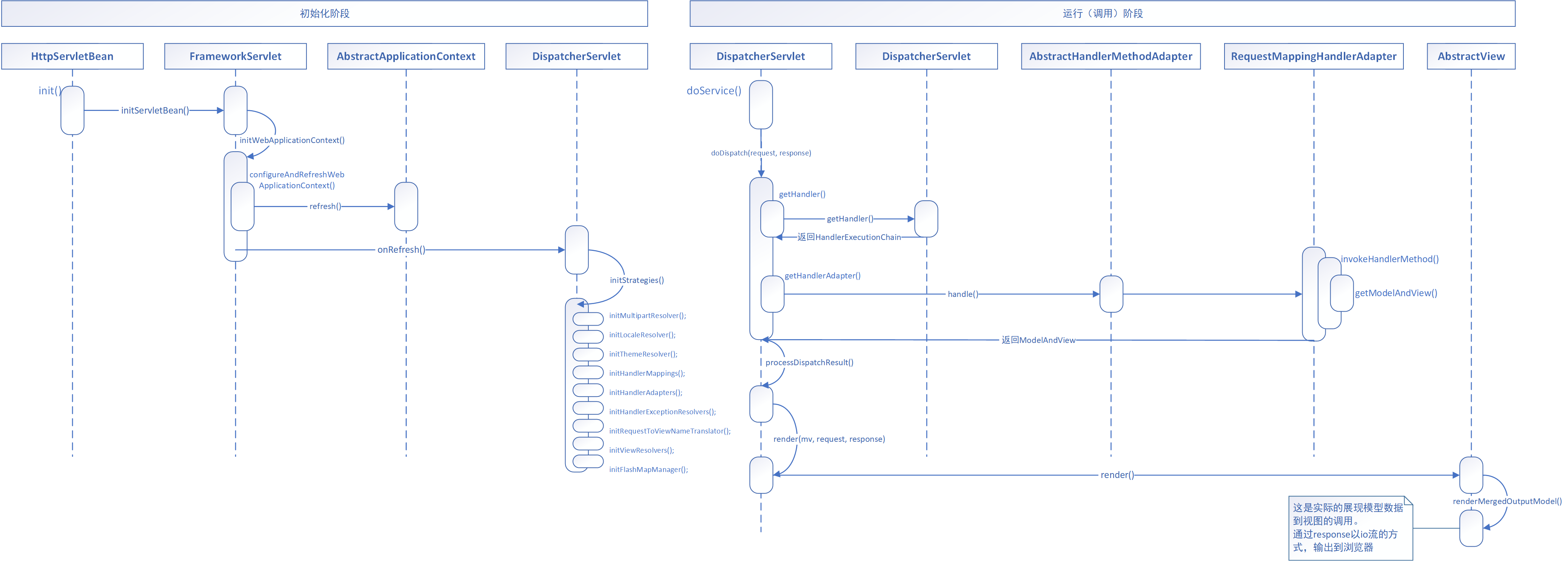
MVC的初始化阶段
DispatcherServlet继承了FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承了HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean里有一个init()方法:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(""Initializing servlet '"" + getServletName() + ""'"");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//定位资源
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//加载配置信息
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error(""Failed to set bean properties on servlet '"" + getServletName() + ""'"", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(""Servlet '"" + getServletName() + ""' configured successfully"");
}
}try…catch…部分主要获取了servlet的配置信息,直接来看来到initServletBean():
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log(""Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '"" + getServletName() + ""'"");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info(""FrameworkServlet '"" + getServletName() + ""': initialization started"");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error(""Context initialization failed"", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error(""Context initialization failed"", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info(""FrameworkServlet '"" + getServletName() + ""': initialization completed in "" +
elapsedTime + "" ms"");
}
}其中initWebApplicationContext():
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//先从ServletContext中获得父容器WebAppliationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
//声明子容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//建立父、子容器之间的关联关系
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//这个方法里面调用了AbatractApplication的refresh()方法
//模板方法,规定IOC初始化基本流程
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
//先去ServletContext中查找Web容器的引用是否存在,并创建好默认的空IOC容器
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//给上一步创建好的IOC容器赋值
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//触发onRefresh方法
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(""Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '"" + getServletName() +
""' as ServletContext attribute with name ["" + attrName + ""]"");
}
}
return wac;
}这个方法里有一个configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法,进入这个方法,发现它调用了Ioc的refresh()方法。
WebApplicationContext和ApplicationContext区别:
-
WebApplicationContext存放的是web相关如Listener、Servlet、Filter、Session、Response、Page等,它继承了ApplicationContext,是ApplicationContext的扩展。
-
ApplicationContext 是 spring 中较高级的容器。和 BeanFactory 类似,它可以加载配置文件中定义的 bean,将所有的 bean 集中在一起,当有请求的时候分配 bean。ApplicationContext 包含 BeanFactory 所有的功能。
进入下面的onRefresh(wac)方法:
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}进入initStrategies(context):
//初始化策略
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//多文件上传的组件
initMultipartResolver(context);
//初始化本地语言环境
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化模板处理器
initThemeResolver(context);
//handlerMapping
initHandlerMappings(context);
//初始化参数适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//初始化异常拦截器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//初始化视图预处理器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化视图转换器
initViewResolvers(context);
//FlashMap管理器
initFlashMapManager(context);
}至此就是MVC的初始化阶段。
MVC的调用阶段
来到DispatcherServlet的doService()方法,它调用了doDispatch(request, response);方法,这是调用的开始。
/** 中央控制器,控制请求的转发 **/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 1.检查是否是文件上传的请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 2.取得处理当前请求的controller,这里也称为hanlder处理器,
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// 如果handler为空,则返回404
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//3. 获取处理request的处理器适配器handler adapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
// 处理 last-modified 请求头
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = ""GET"".equals(method);
if (isGet || ""HEAD"".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(""Last-Modified value for ["" + getRequestUri(request) + ""] is: "" + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 4.实际的处理器处理请求,返回结果视图对象
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 结果视图对象的处理
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException(""Handler dispatch failed"", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException(""Handler processing failed"", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// 请求成功响应之后的方法
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}先看getHandler(HttpServletRequest request)方法:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}返回了一个HandlerExecutionChain,这个对象封装了handler和interceptors。
再来看HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());,此时获取到了处理request的处理器适配器handler adapter。
之后mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());,进入了AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter类,返回的是ModelAndView:
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}进入handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}其中有invokeHandlerMethod,这个方法里有一个getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest)方法,能获取到ModelAndView。
回到doDispatch()方法,继续往下
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
processDispatchResult()方法调用了render(mv, request, response);
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException(""Could not resolve view with name '"" + mv.getViewName() +
""' in servlet with name '"" + getServletName() + ""'"");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException(""ModelAndView ["" + mv + ""] neither contains a view name nor a "" +
""View object in servlet with name '"" + getServletName() + ""'"");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(""Rendering view ["" + view + ""] in DispatcherServlet with name '"" + getServletName() + ""'"");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(""Error rendering view ["" + view + ""] in DispatcherServlet with name '"" +
getServletName() + ""'"", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}进入render方法可以看到,它先解析成为view:view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
然后调用view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
@Override
public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(""Rendering view with name '"" + this.beanName + ""' with model "" + model +
"" and static attributes "" + this.staticAttributes);
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}在这个render()中,调用了renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);,这是实际的展现模型数据到视图的调用。
@Override
protected final void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
T wireFeed = newFeed();
buildFeedMetadata(model, wireFeed, request);
buildFeedEntries(model, wireFeed, request, response);
setResponseContentType(request, response);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(wireFeed.getEncoding())) {
wireFeed.setEncoding(""UTF-8"");
}
WireFeedOutput feedOutput = new WireFeedOutput();
ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
feedOutput.output(wireFeed, new OutputStreamWriter(out, wireFeed.getEncoding()));
out.flush();
}即通过response以io流的方式,输出到浏览器。
至此MVC的调用结束。